What is U.V spectroscopy?
U.V spectroscopy is the measurement of the attenuation of a beam of light passing through a sample or after reflection from sample surface.
Principle of U.V spectroscopy
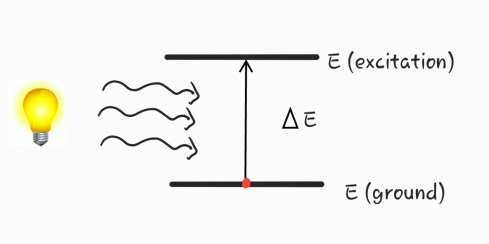
When uv radiation falls on sample the molecules/atoms in the sample gets excited and moves from group state to excited state.
Detector detect the missing wavelength (eting wavelength ) and converts is light signal into electrical signal .
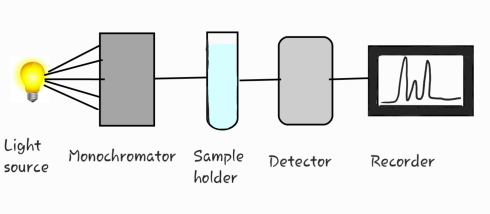
Instrumentation
Components of instrument:
1) light source
2) monochromator
3) sample holder
4) detector
5) amplifier and recorder
1.) Light source
a) Deutrium lamp – u.v region (200- 400nm)
b.) Tugsten halogen lamp – visible region (400-700nm)
2) Monochromator:
Monochromator are device use to resolve wide band of polychromatic light radiation into narrow band of monochromatic radiation.

3.) Sample holder
Cuvette is used as sample holder.
It is made up of quartz.
4.) Detectors
It will convert light energy into electrical signal that are displayed on readout devices.
Barrier layer cell Photo tube
Photomultipliertube
Thermocouple
Balometer
5.)Amplifier and recorder
Amplifier amplifies signal coming from detector and recorder records them which is displayed on readout device.
Process:
1.)Uv radiation first enters into monochromator where polychromatic light gets converted into monochromatic light.
2.) Monochromatic light passes through sample holder containing sample which excites molecules/atoms.
3.) Further the radiation passes through detector where light signal is converted into electrical signal.
4.) The electrical signal are amplified and then send to output device (recoreder).
5.) It is then displayed in the form of graph.
Thank you!